The Impact of Mechanization on Humanity
05/03/2021
|
8 mins to read
|
Share article

TELETUBBIES
Subject: The Impact of Mechanization on Humanity
Yiğit Çakmak (Team Leader)
Evren Çıkrıkçıoğlu
Furkan Çakmak
The Impact of Mechanization on Humanity
Contents
- Subject
- Type of Loss
- Reason for Choosing the Topic for Improvement
- Determining the Goal
- Activity Plan
- Problem Description
- Pareto Analysis of Weak Points
- Risk Assessment
- Pareto Chart
- Fishbone Diagram
- Action Plan
- Explanation of Problem Solution
- Monitoring
- Goal and Comparison
- Standardization
- Dissemination
- Teams to Refer
Subject
The purpose of machines in mechanization should be well evaluated and analyzed.
General objectives are:
- To shorten the time of work and increase productivity
- To use less physical strength and effort
- To enable work in hazardous areas
The following topics will be addressed:
- Determining whether mechanization and new technologies create more new employment opportunities or increase unemployment.
- Investigating whether the era of haste among people is related to machines.
- Researching whether environmental pollution came with mechanization and measuring how much new technologies can play a role in correcting environmental pollution.
- Assessing how many people are affected by the Peltzman effect.
- Investigating which educational levels are affected by the labor shortage caused by mechanization.
- Measuring how mechanization affects cultural differences and customs.
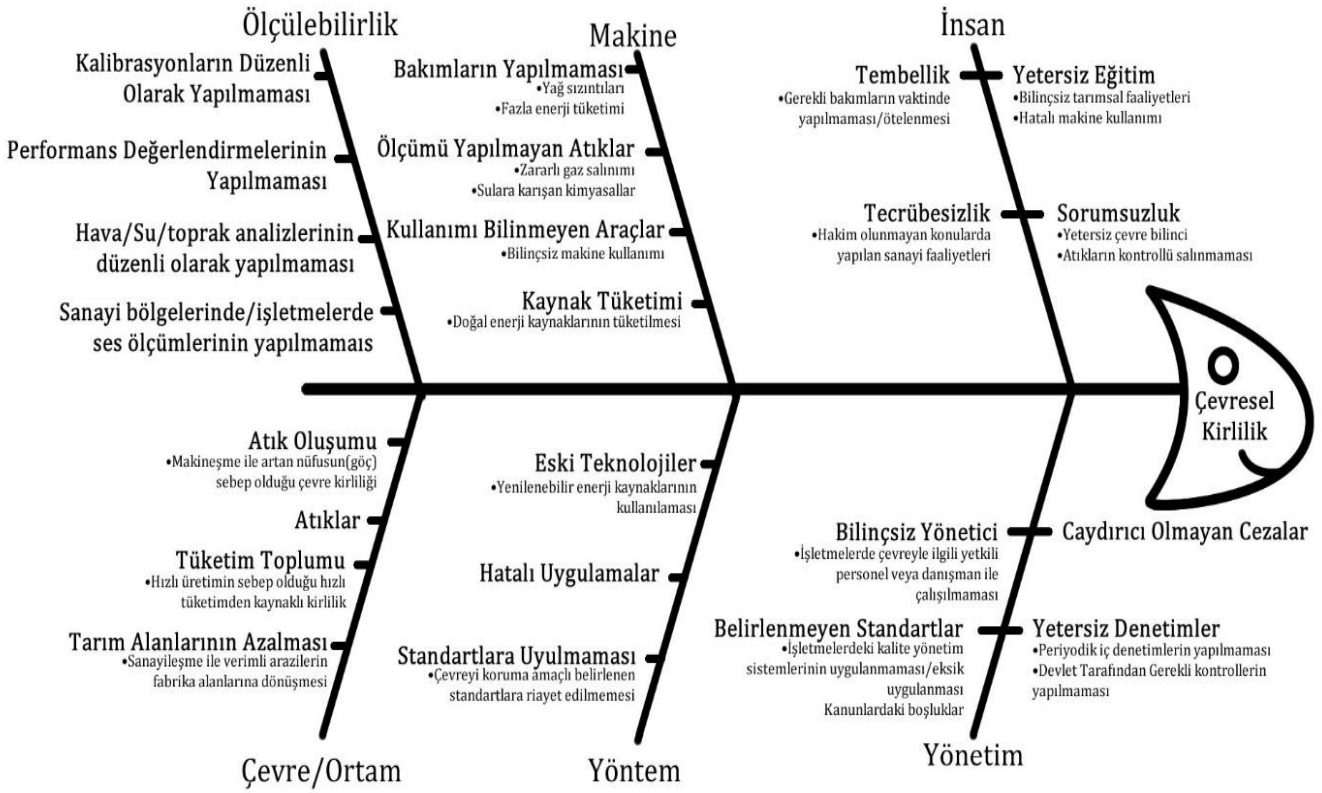
Type of Loss
- Lack of communication and malfunction
- Laziness and machine dependency
- Environmental pollution
- Customs and values
- Economic uncertainty and political instability
- Future anxiety and intense stress
- Negatives of the era of haste
- Employment
- Rapidly changing policies and politics
- Raw materials
Reason for Choosing the Topic for Improvement
- To identify the effects of machines on people and start and determine measures to reduce their negative impacts.
- To determine the extent to which machines contribute to environmental pollution and identify measures to prevent it.
- To initiate guidance for people to new professions due to the unemployment caused by machines in the future.
- To identify the necessary steps for the transition to and adaptation to new technologies by machines.
- To start efforts to maximize the use of minimal physical strength and increase productivity through machines.
Determining the Goal
- Implement measures to prevent environmental pollution and apply ecological systems.
- Redirect the labor gap created by machines replacing people to new professions and sectors.
- Ensure the transition and integration of machines to new technologies.
- Direct people to sports, theater, arts, and various hobbies to prevent laziness from machines.
- Determine necessary short-term policies.
- Increase the efficient use of machines.
Activity Plan
| Planned Task | Responsible | Date |
|---|---|---|
| SWOT Analysis | Yiğit Çakmak | 20.05.2020 |
| SWOT Analysis | Furkan Çakmak | 20.05.2020 |
| SWOT Analysis | Evren Çıkrıkçıoğlu | 20.05.2020 |
| Pareto Analysis | Yiğit Çakmak | 21.05.2020 |
| Risk Analysis | Yiğit Çakmak | 22.05.2020 |
| Bar Chart | Furkan Çakmak | 25.05.2020 |
| Fishbone Diagram | Evren Çıkrıkçıoğlu | 26.05.2020 |
| Identification of Type of Loss | Yiğit Çakmak | 26.05.2020 |
| Reason for Choosing the Topic for Improvement | Furkan Çakmak | 26.05.2020 |
| Determining the Goal | Furkan Çakmak | 26.05.2020 |
| Dissemination | Yiğit Çakmak | 27.05.2020 |
| Goal - Comparison | Evren Çıkrıkçıoğlu | 27.05.2020 |
| Goal - Comparison | Yiğit Çakmak | 27.05.2020 |
| Explanation of Problem Solution | Evren Çıkrıkçıoğlu | 27.05.2020 |
| Action Plan | Yiğit Çakmak | 28.05.2020 |
| Standardization | Evren Çıkrıkçıoğlu | 28.05.2020 |
| Monitoring | Yiğit Çakmak | 28.05.2020 |
Problem Description
A SWOT analysis of the impact of mechanization on humanity has been conducted.
SWOT Analysis
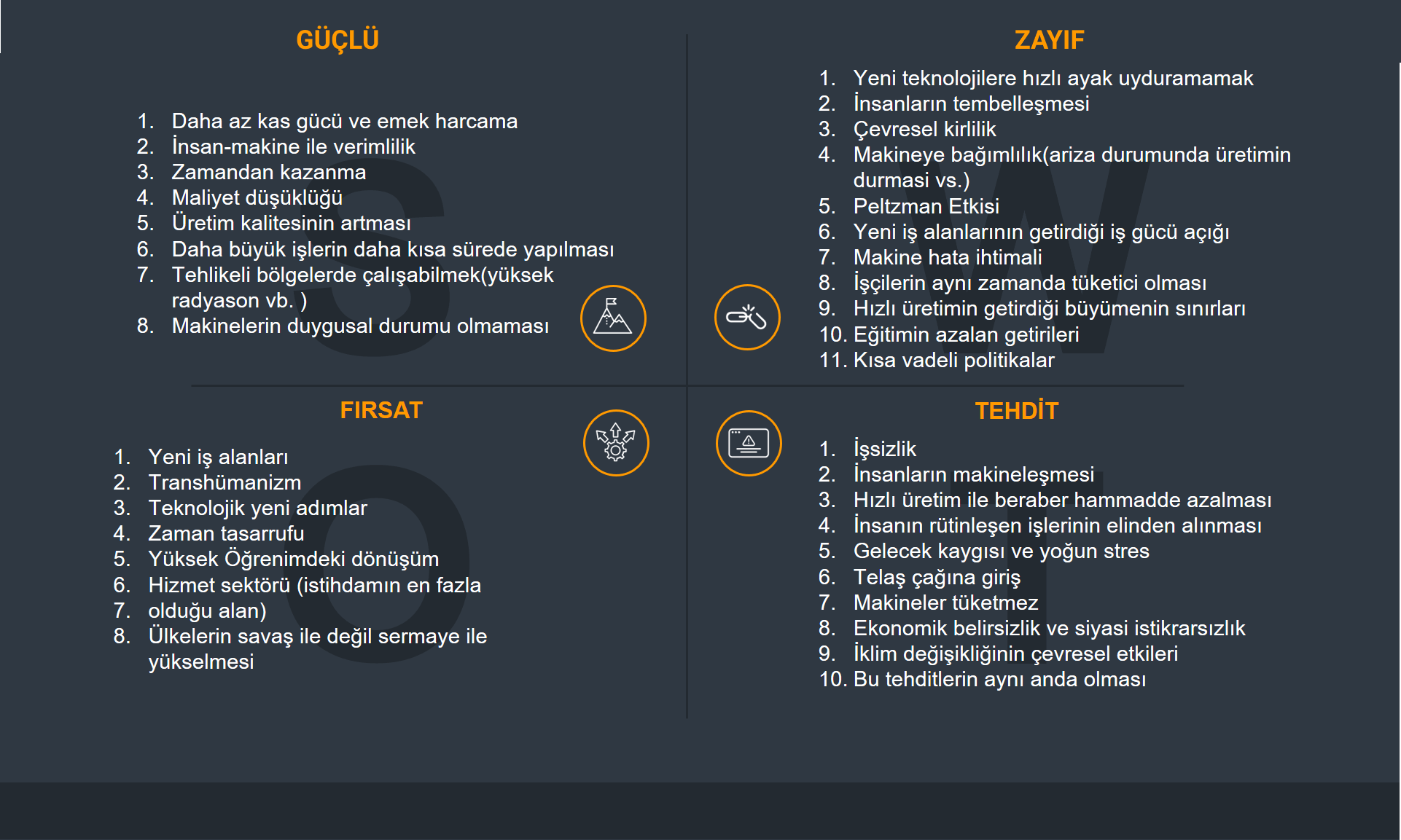
Pareto Analysis of Weak Points
| Weak Point | Yiğit | Furkan | Evren | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Inability to quickly adapt to new technologies. | 4 | 5 | 1 | 10 |
| Laziness of people. | 3 | 3 | 5 | 11 |
| Environmental pollution | 4 | 4 | 5 | 13 |
| Dependency on machines (production halt in case of failure, etc.) | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| Peltzman Effect | 5 | 1 | 3 | 9 |
| Labor shortage due to new job areas | 4 | 2 | 2 | 8 |
| Machine error probability | 1 | 1 | 1 | 3 |
| Workers being consumers at the same time | 2 | 1 | 2 | 5 |
| Limits of growth brought by rapid production | 3 | 4 | 4 | 11 |
| Decreasing returns from education | 3 | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| Short-term policies | 5 | 4 | 4 | 13 |
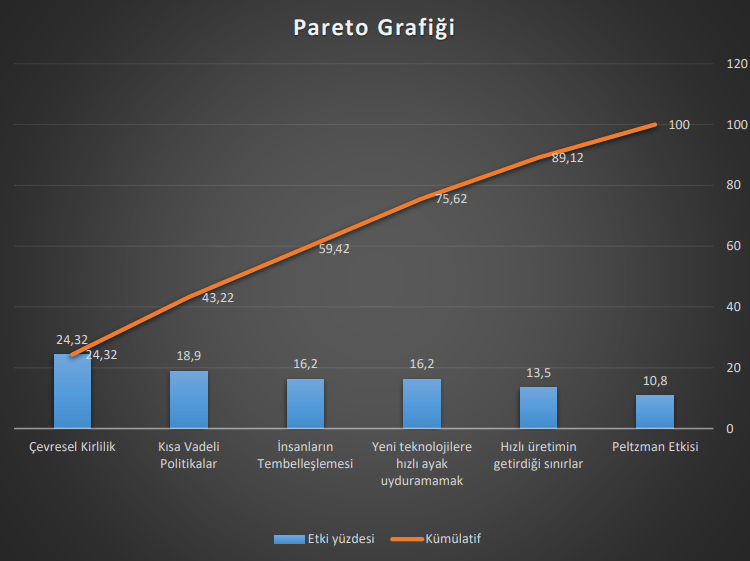
Pareto Evaluation
The weak points from the SWOT application of the impact of mechanization on humanity were rated from 1 (least) to 5 (most), resulting in:
The following table shows the Pareto evaluation (Frequency Evaluation):
| Weak Point | Yiğit | Furkan | Evren | Total |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental pollution | 3 | 3 | 3 | 9 |
| Short-term policies | 3 | 2 | 2 | 7 |
| Limits of growth brought by rapid production | 1 | 2 | 2 | 5 |
| Laziness of people | 1 | 2 | 3 | 6 |
| Dependency on machines (production halt in case of failure, etc.) | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 |
Pareto Evaluation Percentage Values and Cumulative
| Weak Point | Percentage | Cumulative Percentage |
|---|---|---|
| Environmental pollution | 25% | 25% |
| Short-term policies | 20% | 45% |
| Limits of growth brought by rapid production | 15% | 60% |
| Laziness of people | 10% | 70% |
| Dependency on machines (production halt in case of failure, etc.) | 10% | 80% |
Risk Assessment
Definition of Risk Assessment Matrix
The table below separates the risks by Likelihood and Risk Degree. Risk assessment will be based on the following table. For risks with a high risk degree, preventive measures must be taken before the project starts. This way, we also prevent risks arising from the primary risks.
| IMPACT | VERY SEVERE (5) | SEVERE (4) | MEDIUM (3) | LIGHT (2) | VERY LIGHT (1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | 25 | 20 | 15 | 10 | 5 |
| 4 | 20 | 16 | 12 | 8 | 4 |
| 3 | 15 | 12 | 9 | 6 | 3 |
| 2 | 10 | 8 | 6 | 4 | 2 |
| 1 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 |
Risk Assessment Matrix
| Risks | Likelihood | Impact | Risk Level |
|---|---|---|---|
| Environmental Pollution | 15 – 5 | 13 – 4 | 20 / Very High |
| Short-Term Policies | 13 – 4 | 6 – 2 | 8 / Medium |
| Inability to Adapt Quickly to New Technology | 11 – 4 | 6 – 2 | 8 / Medium |
| People Becoming Lazier | 9 – 3 | 13 – 4 | 12 / High |
The impacts of the risks in the highest risk group have been evaluated in terms of duration and cost.
Pareto Chart
Fishbone Diagram
Action Plan
- Reducing environmental pollution: Applying ecological systems and pollution prevention measures.
- Addressing labor gaps: Redirecting labor to new professions and sectors.
- Facilitating technology transition: Ensuring smooth integration and adaptation of new technologies.
- Preventing laziness: Encouraging engagement in sports, arts, and hobbies.
- Formulating policies: Developing short-term and long-term policies to manage the impacts of mechanization.
Explanation of Problem Solution
Solutions for each identified problem have been described and implemented as part of the action plan. These include measures to reduce pollution, manage labor gaps, and facilitate technology adaptation.
Monitoring
Continuous monitoring is essential to ensure the effectiveness of implemented solutions and to make necessary adjustments.
Goal and Comparison
Environmental Pollution
- Air Pollution
- Smoke Pollution
- Chemical Pollution
- Water Pollution
Preventing Pollution
- Measures and strategies for reducing various types of pollution.
Annual Average Waste Generation by Regions
- Data and analysis of waste generation by region.
Medical Waste Generation by Years
- Statistics on medical waste generation over the years.
Standardization
Efforts to standardize processes and practices related to mechanization and its impacts.
Dissemination
Sharing findings and recommendations with relevant stakeholders and the public.
Teams to Refer
- Research and Development Team
- Environmental Impact Assessment Team
- Technology Integration Team
- Public Awareness and Education Team